
The book, which dates from 180 BCE (and is not included in the Jewish canon), includes a list of names of biblical figures ( 44–49) in the same order as is found in the Torah and the Nevi'im (Prophets), and which includes the names of some men mentioned in the Ketuvim (Writings). Sirach provides evidence of a collection of sacred scriptures similar to portions of the Hebrew Bible.

Rabbinic Judaism recognizes the 24 books of the Masoretic Text as the authoritative version of the Tanakh or Hebrew Bible. Both 1 and 2 Maccabees suggest that Judas Maccabeus (around 167 BCE) also collected sacred books ( 3:42–50, 2:13–15, 15:6–9). The Book of Nehemiah suggests that the priest-scribe Ezra brought the Torah back from Babylon to Jerusalem and the Second Temple ( 8–9) around the same time period. The book of 2 Maccabees, itself not a part of the Jewish canon, describes Nehemiah (around 400 BCE) as having "founded a library and collected books about the kings and prophets, and the writings of David, and letters of kings about votive offerings" ( 2:13–15). Some scholars argue that it was fixed by the Hasmonean dynasty (140–40 BCE), while others argue it was not fixed until the second century CE or even later. NY: Facts on File, 1992 "Creating the Canon".There is no scholarly consensus as to when the Hebrew Bible canon was fixed. PA: Jewish Publication Society, 2004 Wigoder, Geoffrey, Ed. Furthermore, the two Bibles differ in their sequence of the texts and writings, as well as the order of importance in the placement of texts. These texts include – 1-4 Maccabees, Judith, and Psalms of Solomon. The Greek Bible includes several additional books, which were not accepted into the Hebrew Bible. The canon of the Hebrew Bible is somewhat different than that of the Greek Bible (which is the basis for the Christian Bible). The conclusion of the last section of the Bible, ketuvim (Writings) is debated however, a majority of scholars believe its final canonization occurred in the second century C.E. The Neviim (Prophets) were finalized during the Persian era, approximately 323 B.C.E. The Pentateuch ( Torah), as we know it today, was completed during the Babylonian exile, by the time of Ezra.
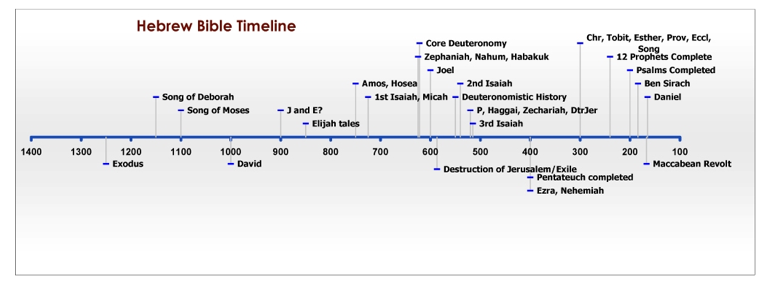
Canonization is the long procedure of collecting and sequencing of the texts in an order of authority and importance. This choosing of texts for the Bible is referred to as canonization, a method of measuring a text’s importance. Nevertheless, there are numerous other texts that never made it into the Bible, many of which are lost today. These texts have become a governing guide for the Jewish people. The books that are found in the Bible were selected on account of their divine inspiration. Jewish Holy Scriptures: Jewish Holy Scriptures: Table of Contents


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
